MRI vs CT Scan: What’s the Difference?
July 17, 2023
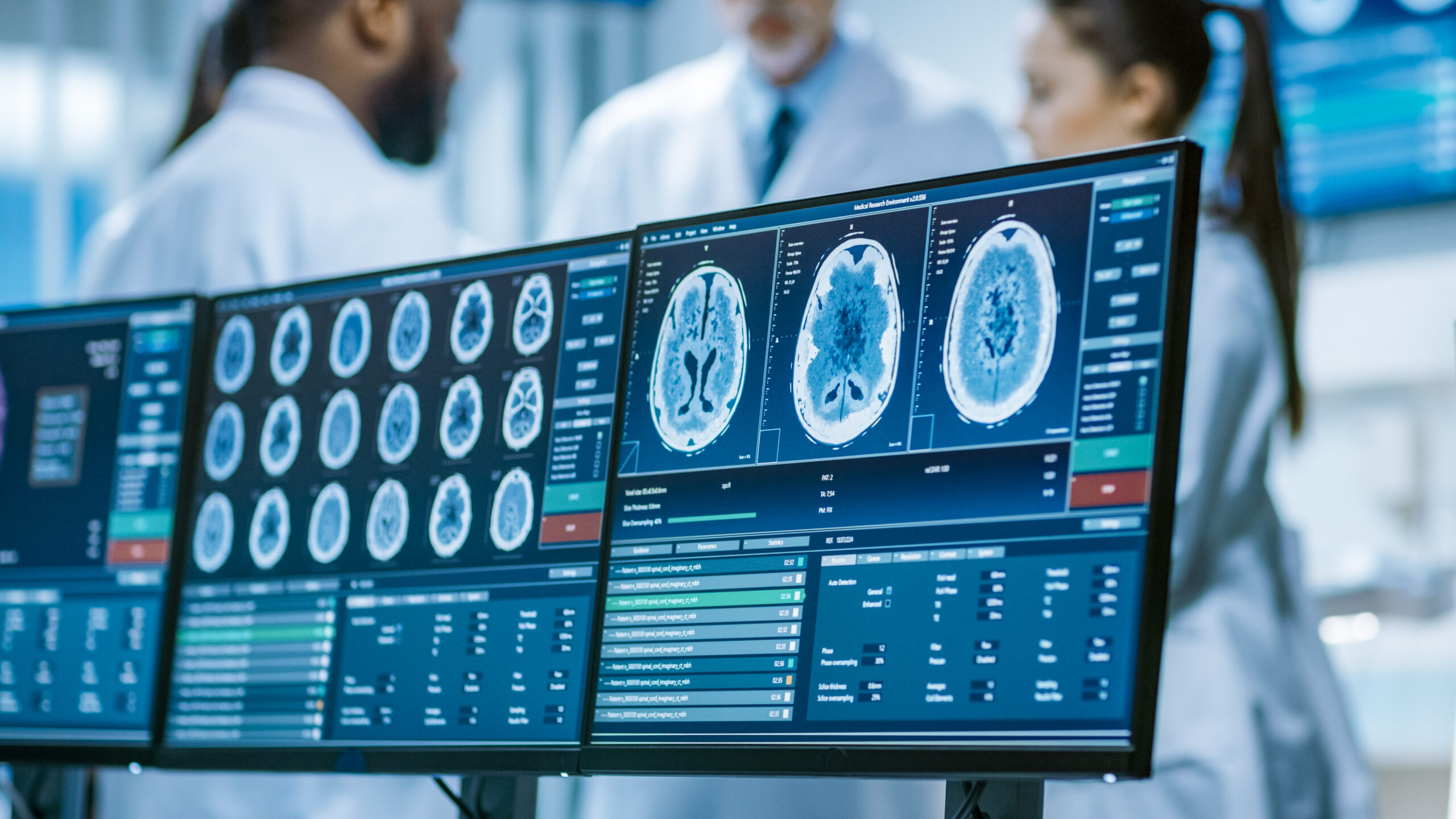
A CT (computed tomography) scan and an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan are both medical imaging techniques that are used to produce detailed images of the inside of the body. However, they use different technologies to produce those images. A CT scan uses X-rays to produce detailed cross-sectional images of the body, while an MRI uses a magnetic field and radio waves to produce detailed images of the body’s internal structures. CT scans are typically faster and better suited for examining bones, while MRIs are better for soft tissue, such as the brain and spinal cord.
What does a CT scan show?
A CT (computed tomography) scan uses X-rays to produce detailed cross-sectional images of the body. It can show a wide range of internal structures, including bones, blood vessels, organs, and soft tissue. CT scans are often used to detect and diagnose injuries and illnesses such as bone fractures, tumours, blood clots, internal bleeding, and infections. They can also be used to guide medical procedures such as biopsies, surgical planning, and radiation therapy. CT scans can also provide a detailed look at the brain, lungs, abdomen, chest, and spine. CT angiograms can be used to show blood vessels and blood flow. CT scans are also used in dentistry, to make a 3D model of teeth and jaws. CT scans are one of the most widely used diagnostic imaging tools because of their speed, high resolution and because they can be used for almost every part of the body.
What does an MRI show?
An MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan uses a magnetic field and radio waves to produce detailed images of the body’s internal structures. MRI does not use ionizing radiation, unlike CT scans. MRI is particularly useful for visualizing soft tissue structures, such as the brain, spinal cord, muscles, ligaments, tendons, and internal organs. An MRA (magnetic resonance angiography) scan can help detect and diagnose blood vessel disorders such as aneurysms and blockages.
What are the benefits of CT scans?
CT (computed tomography) scans have a number of benefits, including speed, as they can be completed quickly, often in less than 10 minutes, which means that patients can be in and out of the imaging center quickly. CT scans produce detailed, high-resolution images that can help doctors detect and diagnose a wide range of injuries and illnesses. CT scans offer versatility as they can be used to examine many different parts of the body, including the head, chest, abdomen, and pelvis, making them a versatile diagnostic tool. Another advantage is the accurate diagnosis they can provide. They’re very accurate in detecting and diagnosing a wide range of injuries and illnesses. CT Scans can be used for guiding medical procedures. They can be used to guide medical procedures such as biopsies, surgical planning and radiation therapy. The lower radiation exposure makes them safe for most people. They’re widely available in most hospitals and diagnostic centers, meaning that patients can usually have a scan done close to home. There’s also the benefit of being cost-effective as they are relatively inexpensive compared to other imaging modalities, making it a cost-effective option for patients and healthcare providers. However, CT scans should be used only when necessary and the benefits outweigh the potential risks, as there is a risk of exposure to ionizing radiation, which can increase the risk of cancer over a lifetime.
What are the benefits of MRI?
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a non-invasive diagnostic tool that can produce detailed images of the inside of the body. Some benefits of MRI include High-resolution images. MRI can produce detailed images of soft tissue, which can help identify abnormalities or injuries that may not be visible on other imaging modalities such as X-ray or CT scan. Since there is no ionizing radiation unlike X-rays and CT scans, MRI does not use ionizing radiation, which means it does not carry the same risks of radiation-induced cancer.
MRI can be used to image a wide variety of body parts and organs, including the brain, spine, joints, and blood vessels. It can detect abnormalities that may not be visible on other imaging modalities. It can be used to monitor the progression or response to treatment of a variety of diseases. It is safe for pregnant women and children. It’s important to note that, sometimes, the procedure may not be suitable for certain patients, such as those with pacemakers
What are the drawbacks of CT scans?
Computed tomography (CT) scans are a diagnostic tool that uses X-rays to create detailed images of the inside of the body. Some drawbacks of CT scans include exposure to ionizing radiation. CT scans use ionizing radiation, which can increase a person’s risk of developing cancer over time, especially if they have multiple scans. There’s also the drawback of the high cost: CT scans can be expensive and may not be covered by all insurance plans. There is also the limited visualization of certain tissues as CT scans are best at visualizing bones and hard tissue, but may not be as good at visualizing soft tissue and organs. There is also the risk of allergic reactions to contrast material for some people which can cause symptoms such as hives, itching, or difficulty breathing. It may not be suitable for certain patients, such as pregnant women and those with kidney problems. It is also not recommended for routine screening, they are mostly used when a specific problem is suspected, or when a treatment is planned.
What are the drawbacks of MRI?
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) has a few drawbacks, including high cost as MRI scans are not covered by government healthcare and are generally higher cost than CT scans. MRI scans have the potential to take longer, depending on the area being scanned and may take up to an hour or more if having multiple scans in one appointment. There is also limited availability because not all hospitals or clinics have MRI machines, so access to this test may be limited in some areas. MRI is not suitable for people with pacemakers and aneurysm clips because the magnetic field can cause the metal to heat up, which can be dangerous. Another drawback is that they’re not suitable for certain conditions such as pregnancy, as the long-term effects of the magnetic field and radiation on a developing fetus are not known.
What injuries require an MRI?
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a useful tool for diagnosing and monitoring a variety of injuries. MRI can help diagnose traumatic brain injuries, such as concussions, as well as other brain conditions, such as tumours or strokes. It can also help identify injuries to the spinal cord and vertebrae, such as herniated discs or fractures. An MRI can help diagnose injuries to muscles, tendons, and ligaments, such as tears or strains. Injuries to joints, such as tears or damage to the cartilage in the knee, shoulder, or hip may require this scan. MRI scans can help identify injuries to organs and other structures in the abdomen and pelvis, such as liver or kidney damage. Finally, breast injuries may require an MRI in order to evaluate breast lumps or abnormalities that cannot be seen on a mammogram.
What injuries require a CT scan?
A Computed Tomography scan is a useful tool for diagnosing and monitoring a variety of injuries. Some injuries that may require a CT scan include head injuries in order to quickly identify skull fractures, bleeding or swelling in the brain, and other traumatic brain injuries. CT scans can identify injuries to the bones of the spine, such as fractures or dislocations, and can also detect any damage to the spinal cord. Chest and abdominal injuries may need scanning to find injuries to the lungs, heart, liver, kidney, spleen, pancreas and other organs in the chest and abdominal area. These scans can identify fractures in bones, even those that may be difficult to detect on X-rays. These procedures can also help identify injuries to blood vessels, such as aneurysms or dissections, and can also help detect blood clots. Another would be sinus and ear injuries, CT scans can be used to evaluate sinus and ear conditions, such as infections or tumours. Finally, the scans can evaluate soft tissue injuries in areas such as the head, face, and limbs.
If you would like to learn more, reach out to us today and get the information you need.